Musculature
All information about "Musculature" and the related magazine articles can be found here.
Our articles are written clearly and link to scientific studies where relevant. This is how we meet our own standards: we regularly deliver new, high-quality content for you—free of charge, no sign-up required, with the highest possible benefit to you.

Taking calcium correctly
Tips on calcium routines & combinations
How can you optimize your calcium intake in everyday life? Read our article to find out which foods are particularly rich in calcium and how you can improve absorption through proper preparation.

Calcium carbonate vs. calcium citrate
A plan for finding the right form of calcium
Team regular meals or spontaneous on the go? Find out which form of calcium suits your lifestyle and what you should look out for when choosing. We'll guide you through the jungle of technical terms.

Interesting facts about calcium
The role of this mineral in the human body
Calcium is a key component of our organism. But what functions does this mineral actually perform in everyday life? Learn more about the physical connections, requirements, and general bone care in our guide.

Calcium and vitamin D3
Your duo for healthy bone metabolism
Calcium is essential for your bones, but without vitamin D3, it often cannot be fully effective. In this article, you will learn why this combination is so important and how you can specifically support your bone metabolism.

Hesperidin against varicose veins
Natural vitality for tired legs
Heavy legs after standing or sitting for long periods? Learn how you can promote your vein health in everyday life. We show you what causes varicose veins and how the plant substance hesperidin can gently support your blood circulation.

Relaxed through winter with PEA
Your gentle companion when the cold bitest
When your shoes resist being put on and the hallway turns into a small ice rink, exercise can still be enjoyable. PEA supports the body's own balance processes, making it easier to step outside and enjoy winter moments with clear air.

Fibromyalgia: living with chronic pain
Living consciously with fibromyalgia – step by step at your own pace
Fibromyalgia is a long-term condition for many, but small rituals can make everyday life noticeably easier. Warmth, relaxation, and loving self-care create moments in which body and soul can find peace.

Vigorously through the flower beds
Your nutrient duo for fall
Anyone who tends flower beds knows that nothing works without strong soil. Collagen and Sango coral are like fertilizer and support at the same time. They give your body the foundation it needs to really blossom in fall.

Magnesium Complex + Vitamin B6 in the evening
Your invitation to rest
Treat your body to the rest it needs after a long day. A magnesium complex with vitamin B6 can help relax your muscles and nerves and gently prepare you for a restful night's sleep.

Stay mineralized when it gets hot
Stay fit through the summer with calcium and magnesium from sango coral
If heat, sweating and circulatory problems are getting to you, a good supply of minerals is crucial. Find out here how calcium and magnesium from sango coral can support you naturally.

Light legs, light day. How horse chestnut, vitamin C and OPC help against heaviness
Discover how proven plant extracts and vitamins can relieve the feeling of heavy legs. For more lightness in everyday life for mom, grandma & co.
Heavy legs after a long day? Horse chestnut, vitamin C and OPC can promote blood circulation, strengthen the veins and noticeably relieve the feeling of tired, weighed-down legs. Ideal for anyone who stands a lot, walks a lot or simply wants to stay active in everyday life. Whether mom is out shopping or grandma is out for a walk. Find out how these natural active ingredients support your leg health and give you new lightness.

Start your vacation full of energy with potassium & magnesium citrate
How to keep you and your family fit, active and balanced even in the heat
On summer vacation, electrolytes such as potassium and magnesium quickly become unbalanced. This can affect energy, muscles and concentration. Find out here how you can strengthen your inner balance with smart nutrition and targeted supplements.

Naturally powerful: Turmeric, boswellia & ginger
Learn how to gain more zest for life with plant power
Plant-based active ingredients can help to reduce inflammation and make everyday life more active and mobile - whether in the garden, during sport or on a family outing.

Moving through spring: supporting joints naturally with MSM, glucosamine and chondroitin
Find out how your joints work - and how targeted nutrients, exercise and high-quality supplements can promote your mobility.
Movement is often difficult after winter. Stiff joints and limited range of motion are not uncommon. Natural active ingredients such as MSM, glucosamine and chondroitin can help to support normal joint function and prevent discomfort. Now is the ideal time to get going with renewed energy. Moving, vital and well nourished into spring.

Activate metabolism for more energy with L-carnitine & omega-3
How to keep your body active without dieting stress
Spring is calling, and with it comes the desire for more energy and a fit body. L-carnitine and omega-3 fatty acids can gently support your metabolism by boosting fat burning and reducing oxidative stress. Find out why now is the perfect time to give your system a boost!

Citrulline – the natural energy booster
Find out how citrulline can help support your performance and endurance in everyday life.
Citrulline can support your energy and endurance, promote recovery and improve blood flow. Discover how this amino acid derivative can help you in your daily life.
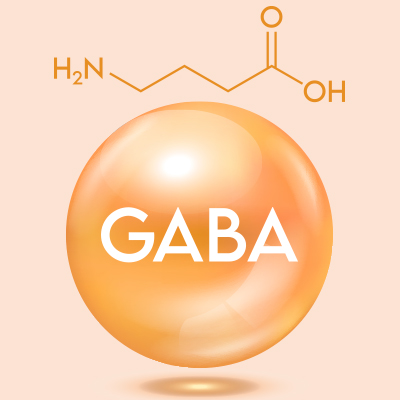
Say goodbye to stress - hello GABA!
Do you often feel stressed and overworked? GABA, a natural neurotransmitter, could be the solution. Find out how GABA helps your body to reduce stress, calm your nerves and promote a feeling of deep relaxation.

D-Ribose - a natural power up
From the muscles to the heart: D-ribose is of great importance for our health and performance. As a component of all human cells, it is essential for the body's energy supply and regeneration. Health-conscious people and athletes therefore rely on this natural option to support their vitality and their cells. Find out more about D-ribose here now!

How creatine affects fitness
Creatine is primarily known for its effect on muscle building - but it plays a far more versatile role in the human body. We have summarised everything you need to know about this special substance for you in this article.

How L-carnitine works in energy metabolism
Carnitine is mainly found in animal foods and plays an important role in energy metabolism. Find out more now.

About vitamin B12 deficiency and pain
We all know that B vitamins are very important for our health. But many people don't realise how serious a vitamin B12 deficiency can be! Not just for vegetarians, vegans, pregnant or breastfeeding women, diabetics or even alcohol drinkers!

L-threonine - an essential amino acid with important functions
Amino acids are an important building block for our health. Which ones can the body produce and which ones need to be ingested in order to fulfil all functions? What are the risks for vegans and what are the dangers of a deficiency? Our report answers the most important questions!

Fitter and stronger with L-Carnosine?
Although carnosine can be produced by the human body, it is a popular supplement among athletes - in powder or capsule form. In this article, you can find out what specific effects it has on performance and what other functions it is involved in.

Magnesium: How does it affect the menstrual cycle?
Many women are familiar with them and suffer from them every month: Menstrual cramps. Read more about the processes in your body during your period, discover natural approaches to relieve the pain and find out what role magnesium and other nutrients play in this. Improve your quality of life during your period in a completely natural way!
Muscles: the powerhouses of our body
Have you ever wondered what keeps your body moving? What makes you able to stand up, walk or even just smile? The answer lies in a fascinating system that runs through every corner of your body: the muscular system.
If you want to learn more about your muscles and discover fascinating facts about important organs, you will find all the information you need here.
Simply explained: What is a muscle?
You can think of a muscle as a kind of biological motor. It is a contractile organ that can contract and relax. This ability enables us to move, stand upright and even breathe. Muscles respond to electrical impulses and convert them into mechanical work. They are true all-rounders in our body and ensure that we can actively move and interact in our environment.
The three muscle types: a perfect trio
Our body has three different types of muscles, each of which fulfills specific tasks.
Striated skeletal musculature
This makes the skeletal muscles the largest contractile organ in the human body. As the name suggests, the skeletal muscles are connected to our skeleton and enable us to do things like run, jump and wave. Every skeletal muscle is under our conscious control. However, we need tendons for our muscle power to be transferred to our skeleton. Every tendon plays a crucial role in the connection and cooperation between muscles and bones: they are attached at one end to the muscle and at the other to the bone, thereby ensuring the transmission of force.
Smooth muscle of the internal organs
We distinguish smooth muscle from skeletal muscle. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs such as the intestines or blood vessels. It works automatically and cannot be controlled at will. To be more precise, it is controlled by the autonomic nervous system and adapts to the body's needs. Among other things, the smooth muscle of the internal organs ensures that our digestion works smoothly.
Heart muscles
As the name suggests, this special type of muscle forms your heart. It is also striated, but works involuntarily and rhythmically. The heart muscle tirelessly pumps blood throughout your body. It is unique in its ability to work for a lifetime without a break and to supply itself with energy.
How many muscles does the human body have?
It may be hard to believe, but the human body actually consists of around 656 muscles! These make up about 40% of the total body mass for men and about 32% for women. Each of the 656 muscles has a specific task and helps to ensure that your body functions smoothly.
From the tiny muscles in your inner ear to the large muscles in your legs, each one plays an important role in the complex machinery of our body.
How is a muscle structured?
Let's zoom into a muscle to take a closer look at the anatomy: the smallest functional unit of a muscle is the sarcomere. Many sarcomeres form a myofibril, and many myofibrils form a single muscle fiber or muscle cell. These combine into larger units that ultimately form the entire muscle.
The muscle fibers are surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endomysium. Several muscle fibers form a primary bundle, which is surrounded by the perimysium. A group of these primary bundles forms a secondary bundle. The entire muscle is enclosed in a muscle fascia called the epimysium.
This complex structure allows the muscle to develop strength while remaining flexible. The various layers of connective tissue ensure that the force is distributed evenly and that the muscle does not tear when it is under strain.
How do muscles work?
Every muscle movement begins with an electrical impulse. This impulse is transmitted from the brain via the nerves to the motor end plate of the muscle. There, the messenger substance acetylcholine is released, triggering an action potential in the muscle fiber.
As a result, the calcium concentration in the muscle fiber increases. This in turn causes the actin and myosin filaments to slide into each other: the muscle contracts. This process is called the sliding filament theory and is the reason why your muscles can move.
Muscle contraction is an energy-intensive process. The energy for this is supplied by the energy carrier ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Depending on the intensity and duration of the muscle work, various energy supply systems are activated, from rapid anaerobic energy production to long-term aerobic energy supply.
More than just movement: what other tasks do muscles fulfill?
Our muscles are true all-rounders. In addition to their obvious function of movement, they fulfill numerous other important tasks:
- Heat production: Muscles generate heat when they work, thus helping to regulate body temperature. About 85% of body heat is generated by muscle activity.
- Metabolism: Muscles are active metabolic organs. They produce so-called myokines, messenger substances that fulfill important functions in the body. Among other things, myokines influence fat and sugar metabolism and have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Protection: Muscles protect internal organs and stabilize joints. They provide a kind of natural armor for our body.
- Posture: Skeletal muscles enable us to stand upright. Without them, we would literally collapse in on ourselves.
- Energy storage: Muscles store glycogen, a form of carbohydrate that can be quickly converted into energy.
Table of contents of particularly important muscles
Some muscles in our body deserve special attention. These include:
- Latissimus dorsi: The latissimus dorsi (lat. for “large back muscle”) is the largest muscle in the human body. It covers a large part of your back and is important for arm movements and spinal stability.
- Gluteus maximus: The gluteus maximus (large buttock muscle) is the largest muscle in terms of volume. It plays a crucial role in walking, running and climbing stairs.
- Masseter: The masseter (jaw muscle) is the strongest muscle in relation to its size. It develops enormous power that allows you to crush hard food.
- Sartorius muscle: The sartorius muscle (Musculus sartorius) is the longest muscle in the human body. It runs diagonally across the thigh and helps with flexion of the hip and knee joints.
Why muscle training is useful
Regular exercise is the key to healthy and strong muscles. Strength training can help you build muscle and improve your performance. But endurance training is also important because it promotes blood flow to the muscles and improves their efficiency.
However, there are a few things to keep in mind. For example, every muscle has an antagonist. So when you flex your biceps, your triceps automatically relax. That's why a balanced workout is important to avoid imbalances. If you exercise regularly, your body will automatically adapt to the demands through adaptive mechanisms. These mechanisms include:
- Hypertrophy: The muscle fibers become thicker.
- Neural adaptation: The control of the muscles by the nervous system improves.
- Metabolic adaptation: The metabolism in the muscles becomes more efficient.
- Hyperplasia: The number of muscle fibers increases. However, this point is scientifically controversial [1].
If you want, you can support muscle growth with substances like creatine. Incidentally, regular exercise not only boosts muscle growth but can also support the immune system.
Muscle diseases: when the powerhouse goes on strike
Unfortunately, muscles can also be affected by diseases. The most common muscle diseases include:
- Muscular dystrophies: Inherited disorders that cause progressive muscle wasting [2]. The best known form is Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
- Myositis: Inflammatory diseases of the muscles. They can be caused by autoimmune reactions or infections [3].
- Fibromyalgia: A chronic disease characterized by widespread muscle pain. The exact causes of fibromyalgia are not yet fully understood [4].
- Myasthenia gravis: an autoimmune disease in which the transmission of nerve impulses to the muscles is disrupted [5].
- Rhabdomyolysis: an acute breakdown of muscle fibers that can lead to severe complications [6].
If the symptoms persist, you should always consult a doctor to determine the cause and to start appropriate treatment as soon as possible.
Our muscles: a marvel of nature
From the smallest muscle fiber to the largest muscle: our body is a unique system of strength and movement. Our musculature not only allows us to move, but also contributes significantly to our health and well-being.
It is no wonder, then, that researchers are also keen to learn more and more about our muscles. Among other things, scientists are working on restoring damaged muscle tissue using stem cell therapies or tissue engineering. This could give new hope in the future to patients with severe muscle injuries or degenerative muscle diseases [7].
Research is also currently being conducted into the development of exoskeletons and prostheses that are directly connected to the muscles and nervous system. This could help people with paralysis or amputations to regain lost mobility [8]. Research into the molecular mechanisms of muscle contraction, on the other hand, could lead to new therapies for muscle diseases.
Whether you are a professional athlete or just want to get through your daily routine, you couldn't do it without your muscles. So take good care of them, challenge them regularly and enjoy the achievements your body is capable of. From now on, there's no more listlessness!
Sources:
[1] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8107539
[2] https://hirnstiftung.org/muskeldystrophien
[3] https://www.dgm.org/myositis
[4] https://vita-world24.de/Fibromyalgie-Leben-mit-chronischen-Schmerzen
[5] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15891271
[6] https://flexikon.doccheck.com/Rhabdomyolyse
[7] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31042682
[8] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34756339
