Secondary Messengers
All information about "Secondary Messengers" and the related magazine articles can be found here.
Our articles are written clearly and link to scientific studies where relevant. This is how we meet our own standards: we regularly deliver new, high-quality content for you—free of charge, no sign-up required, with the highest possible benefit to you.

Glycine regenerates body and mind
As an important amino acid, glycine is involved in many processes in the body and can have a positive effect on both physical and mental health. Muscles, skin, stress and psyche: find out more about the extensive areas of application and effects of this amino acid here.

How to recognise the symptoms of a vitamin deficiency
Permanent tiredness, mood swings, digestive problems and hair loss - vitamin deficiency can manifest itself in many unspecific symptoms. Find out which ones you shouldn't ignore.

Is Moringa a real "superfood"?

This is how versatile the micronutrient choline is in the body
The vitaminoid is a real all-rounder & is used in many places in the body as a cell building block. A deficiency has major health implications.

Omega 3 for your skin, heart and brain
Omega-3 fatty acids are found in some foods, including fish. If you have an unbalanced or vegetarian diet, omega-3 capsules are a sensible alternative to ensure you get enough of the fatty acid. Find out more about the many benefits of an optimal omega-3 intake and how a deficiency can become apparent.

Reishi - a medicinal mushroom with thousands of years of tradition
What makes Reishi so special? Reishi has a long history in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and is now gaining popularity worldwide as a medicinal mushroom with positive health effects. Find out more about its many uses, the scientific research and the potential benefits attributed to it.

How L-carnitine works in energy metabolism
Carnitine is mainly found in animal foods and plays an important role in energy metabolism. Find out more now.

These are the causes of hair loss
There are many different types of hair loss in men and women - and there are different ways to help your hair grow back. Find out more now.

Vitamin K2 for bones and cardiovascular health
A vitamin K2 deficiency is associated with osteoporosis and arteriosclerosis. Here you can find out more about this important vitamin, its function in calcium metabolism and what you should definitely bear in mind when taking a supplement.
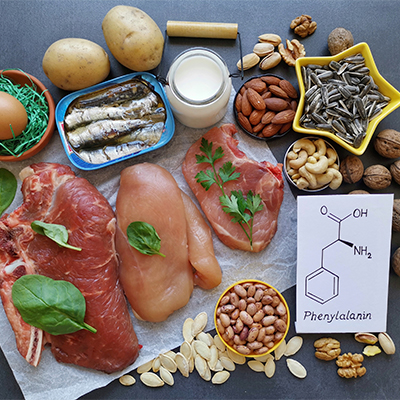

The body needs phenylalanine for this
The amino acid phenylalanine is required for the synthesis of dopamine and serotonin and is also an important building block for proteins. Find out more now.
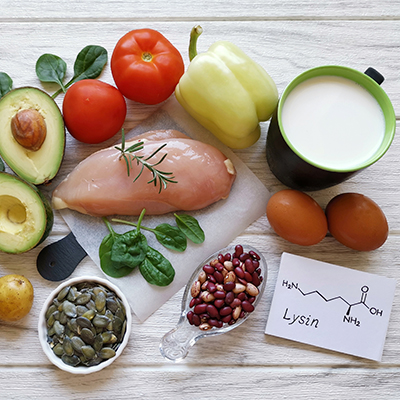

The essential amino acid lysine
From the metabolism to the immune system to the skin: there are many processes in the body in which lysine is involved. A deficiency of the essential amino acid can therefore disrupt these processes. The good news is that lysine is found in many foods. Find out more in this articel!

Your nutritional timetable for pregnancy
The right diet is particularly important during pregnancy to ensure that the expectant mother and, above all, the baby are adequately supplied with all the important nutrients. Because nutrition can influence the baby's development! Valuable answers and tips can be found here.

The importance of beta-glucan for the body
Good for the gut and the immune system? Fibre is said to have a number of health-promoting properties and effects. We have summarised these for you in this article.
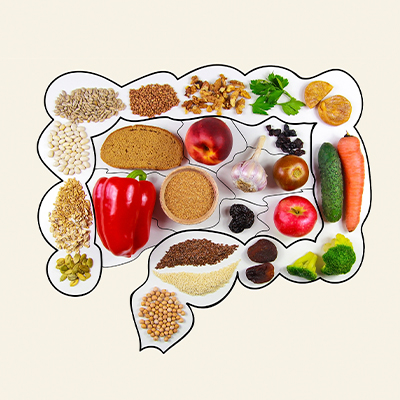

Propionic acid - why we need vegetables for this
Everyone has heard that fibre is important for our health, but do you know why? Did you know that vegetables and pulses form propionic acid in our gut? But what is it good for? Find out more here!

Selenium - effect, deficiency and overdose!
The trace element selenium, which is essential for us, plays a supporting role throughout the body - whether in numerous metabolic processes or a healthy thyroid gland. However, the low content of selenium in our food is often not enough to ensure an adequate supply. What exciting findings have scientists made with it in research and how is it linked to Hashimoto's? Selenium deficiency or overdose - how bad is it in each case? Read more about it here!

Guarana - a good coffee alternative?
Is guarana a real alternative to your morning cup of coffee? The extract from the superfruit from the tropics is becoming increasingly popular as an additive for drinks and as a supplement.

All you need to know about caffeine tablets
Caffeine tablets are a convenient and fast-acting way to get the energy boost of caffeine without drinking a cup of coffee or other caffeinated beverages. Find out more now.

Brown algae - nutrients and vitamins from the sea
Inconspicuous and widely underestimated: brown algae are not only tasty as food, but also a good way to support your body as a dietary supplement. Find out everything you need to know about the benefits of these algae here.

Turmeric - more than just a spice
Turmeric is still very popular today. What is the truth behind the phenomenal effects attributed to this yellow tuber?

The underrated power of folate: Why this vitamin is so important

B6 - a vitamin with many tasks!
The water-soluble vitamin cannot be stored by the body, but is extremely important for us! It is essential for metabolic processes, nerve transmission, hormone production, the immune system and also for regulating homocysteine levels! But despite a balanced diet, are you at risk of vitamin B6 deficiency? Maybe it's due to the contraceptive pill! Read more about this here!

Why is methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) so important to us?
An adequate supply of sulphur is essential for the proper functioning of enzymes and amino acids. Here you can read about the benefits of MSM for our skin and hair, as well as for osteoarthritis, allergies and sports injuries.

Getting all the vitamin B12 you need in a vegan diet
Those on a vegan or vegetarian diet should pay more attention to whether they have an adequate supply of vitamin B12. Find out more now
Get rid of bladder infections!
Almost every woman has had a urinary tract infection, and some suffer from it regularly. Find out why we should take this infection seriously, how it develops and what types of treatment are available!
Messenger substances: our body's own communication experts
Imagine entering a huge house with billions of rooms. Employees sit in each of these rooms, constantly communicating with each other to keep the entire building running. This is exactly how you can imagine your body, with the rooms representing the cells and the employees representing the various organs and tissues.
But how exactly does this communication work? This is where the messenger substances come into play – our body's own communication experts.
What are messenger substances?
Messenger substances, also known as chemical messengers, are molecules that transmit information between cells. They are used by living beings for signal transmission or chemical communication (chemocommunication). Messenger substances are fundamentally important for the interaction and communication between cells and tissues within an organism. They are, so to speak, the language with which our body communicates internally. Neurotransmitters, for example, are special messenger substances that play a central role in the nervous system, especially in the brain.
How do messenger substances differ from hormones?
Hormones are a special type of messenger substance that are produced by endocrine glands and released directly into the blood to exert their effect on distant target organs. The main difference lies in their range of action:
- Hormones act systemically throughout the body, while other messenger substances often have a local effect.
- While all hormones are messenger substances, the opposite is not true. There are many messenger substances that are not hormones, such as neurotransmitters in the brain.
- Hormones are released into the blood and can thus act throughout the body, while other messenger substances, such as neurotransmitters, are often only active in limited areas, such as at synapses between nerve cells.
What are the best-known neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are special messenger substances that play a central role in the nervous system, particularly in the brain. They transmit signals between nerve cells and thus control our thoughts, feelings and actions. The best-known neurotransmitters include serotonin, often referred to as the “happy hormone” because it has a strong influence on our mood and well-being. Healthy serotonin levels are crucial for preventing depression and anxiety [1].
Another essential neurotransmitter is dopamine, which is responsible for motivation and reward; a deficiency or imbalance can lead to problems such as listlessness or addictions. Acetylcholine, on the other hand, is important for muscle contraction and cognitive function, especially memory, while GABA, as an inhibitory neurotransmitter, has a calming effect and helps us to cope with stressful situations. The balance of these neurotransmitters is crucial for our mental and physical health and they illustrate how complex our internal communication via chemical agents is organized.
How many messenger substances are there?
It is difficult to say exactly how many messenger substances there are, as research is constantly discovering new ones. In the brain alone, we now know of more than 100 different neurotransmitters. In addition, there are numerous hormones and other signaling molecules in the body. These range from simple amino acids to complex peptides. This diversity enables the human body to react precisely.
From production to effect: the path of a messenger substance
The path of a messenger substance involves several important steps, from its production to its effect in the target cells:
- Production: Messenger substances are produced in special cells.
- Storage: Many messenger substances are stored in vesicles (small bubbles).
- Release: A signal triggers the release of the messenger substance.
- Transport: The messenger substance moves to its target cell.
- Binding: At the target cell, the messenger substance docks onto specific receptors.
- Effect: The target cell reacts to the signal.
- Degradation or reuptake: The messenger substance is degraded or transported back to the cell of origin.
This complex process takes place millions of times in our bodies and enables us to react to our environment, to feel emotions and to adapt our behavior.
What are the tasks of messenger substances in the human body?
Messenger substances control almost every aspect of our lives:
- Metabolism: Hormones such as insulin regulate our energy balance and help control blood sugar levels.
- Emotions: Neurotransmitters such as serotonin influence our mood and play an important role in the development of depression.
- Pain sensation: Endorphins, our body's own painkillers, are released when we feel pain and can lead to a feeling of euphoria.
- Sexuality: Hormones such as testosterone and estrogen control our sexual development and behavior. They influence not only physical characteristics but also libido and fertility.
- Learning and memory: Acetylcholine plays an important role in cognitive processes and is crucial for the formation of new memories.
- Sleep-wake cycle: Melatonin regulates our sleep cycle and is influenced by light.
Messenger substances in nature: from honeybees to insects
Humans are not the only ones to use chemical signals for communication: honeybees, for example, communicate via pheromones to coordinate the swarm. These chemical signals help them find food sources and signal danger.
In many insects, chemical signals play a role in finding a mate. Some butterfly species can detect the pheromones of potential mates over a distance of several kilometers.
Plants also release messenger substances to defend themselves against pathogens. They can even warn neighboring plants when pests attack.
How messenger substances affect our health
It is now clear that messenger substances are important for our health. It is therefore only logical that an imbalance of messenger substances can lead to various illnesses [2]:
- Depression is often associated with a serotonin deficiency. This leads to therapeutic approaches that aim to increase serotonin levels in the brain.
- In Parkinson's disease, dopamine-producing cells die, leading to the characteristic movement disorders.
- Diabetes occurs when the body does not respond properly to the hormone insulin or does not produce enough of it.
- Thyroid disorders are often due to an over- or underproduction of thyroid hormones.
What influence do drugs have on the messenger substances in our body?
Drugs have an extreme effect on our neurochemical processes and influence the finely tuned balance of our neurotransmitters. One example is cocaine, which blocks the reuptake of dopamine. This leads to an intense feeling of happiness, but in the long term it can lead to the exhaustion of the dopamine system.
Opiates work by binding to the same receptors as our body's own endorphins. This binding explains not only their pain-relieving effect but also their high addictive potential. Regular use can cause the body to become accustomed to the drug, requiring ever-higher doses.
Alcohol, on the other hand, has a complex effect because it influences various neurotransmitter systems. For example, it enhances the effect of GABA, which leads to its calming effect. At the same time, it inhibits the activity of glutamate, which increases the dampening effect on the central nervous system.
How are genes and messenger substances related?
Neurotransmitters such as dopamine play a crucial role in signal transmission in the nervous system and can subsequently regulate the activity of certain genes. In extreme cases, this can even influence cognitive performance such as intelligence. Particularly interesting in this context is the epigenetic regulation of genes that code for dopamine receptors.
This regulation can be triggered by various environmental influences, such as stress. Such external factors can cause epigenetic changes in genes via messenger substances and significantly influence their activity [3]. These findings not only help us to understand how our brain works, but also open up new perspectives for understanding and possibly treating neurological and psychiatric disorders in which gene regulation plays an important role.
Messenger Substances and Nutrition
Our diet plays a crucial role in influencing the production and effect of neurotransmitters, which in turn significantly determines our physical and mental well-being and influences how much energy we have. Tryptophan, an essential amino acid and precursor of serotonin, is found in protein-rich foods such as chicken, turkey and nuts. This compound is important because it supports the body's production of the “happy hormone” serotonin, which is crucial for our mood and emotional balance. Omega-3 fatty acids, found primarily in fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel, also promote the function of neurotransmitters and can potentially help prevent depression by supporting brain health.
Equally important is vitamin B6, which is found in foods such as whole grains, bananas and potatoes, as it supports the production of numerous messenger substances and thus strengthens the nervous system. A balanced and nutritious diet thus ensures that the synthesis and effect of messenger substances is optimal, which directly contributes to a better sense of well-being and an overall healthier lifestyle.
What does stress have to do with messenger substances?
Stress activates various messenger substances in our body:
- Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, is released in stressful situations and prepares the body for fight or flight.
- Adrenalin, another stress hormone, increases heart rate and blood pressure and mobilizes energy reserves.
Chronic stress is a challenge for our body, can lead to an imbalance of these messenger substances and impair our health in the long term.
Messenger substances in the course of life
From birth to death, the production and effect of many messenger substances changes:
- The production of growth hormones decreases, which leads to changes in muscle development and fat distribution.
- The levels of sex hormones such as estrogen and testosterone decrease, which triggers the menopause or andropause.
- The sensitivity of receptors can decrease, which affects the effectiveness of messenger substances.
Messenger substances hold our biological system together
Neurotransmitters are the invisible threads that hold our complex biological system together: from controlling our daily functions to our deepest emotions, they are involved in everything. Neurotransmitters are the basis of our lives, our feelings and our experiences. And every day we learn more about the important chemical messengers that make us who we are.
Research into neurotransmitters has revolutionized our understanding of the human body and is constantly opening up new possibilities in medicine and science. From the development of new drugs to insights into the emergence of consciousness, neurotransmitters play a central role in all areas.
Sources:
[1] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31002895/
[2] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37385351/
[3] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19259783/
