Amino Acids
All information about "Amino Acids" and the related magazine articles can be found here.
Our articles are written clearly and link to scientific studies where relevant. This is how we meet our own standards: we regularly deliver new, high-quality content for you—free of charge, no sign-up required, with the highest possible benefit to you.

Tryptophan - for wellbeing and sleep
Your building block for serenity and a good night's sleep
When the clock changes, your body needs clear signals. Discover how the essential amino acid L-tryptophan, a precursor to serotonin and melatonin, can gently guide your internal clock and help you cope with the time change without noticeable mini-jet lag.

Focus instead of brain fog
Get through your day with acetyl-L-carnitine
Keep a clear head despite a busy schedule! Stay in the flow, stay calm, and get through the day—with acetyl-L-carnitine backing you up. Find out more here!

Your kitchen helper bromelain
Eat hearty meals without feeling heavy
Sometimes feeling heavy can get in the way of enjoyment. Discover how you can strike a balance between hearty meals and a light stomach with the enzyme bromelain and a conscious diet.

Sleep better with GABA
The key to your inner peace
Discover how GABA can act as an “inner brake” and contribute to restful sleep. Learn how to balance your sleep-wake cycle with simple tips and rituals.

Between resting mode and new beginnings: L-threonine in focus
When your head is still barefoot but your calendar is already wearing sneakers
L-threonine suits this in-between time like iced coffee suits late summer: subtle, but just right. Discover how the silent amino acid can give your system gentle structure - in the middle of the transition.

Sleep better with lemon balm, passionflower and L-theanine
These natural helpers bring peace to your evening
Sleep disorders? Stress in the evening? Herbal helpers such as lemon balm, L-theanine and passionflower can gently support the sleep-wake rhythm and help you to finally calm down. Read the article now to find out how you can harness the power of nature for restful nights.

Spring fever for the soul
Naturally more balance with 5-HTP, L-tryptophan and vitamin B6
The sun is shining - but everything still feels heavy inside?
These three mood boosters gently help you arrive in spring: for more rest, sleep and stability. Find out more here!

Start spring naturally fit with L-citrulline & cordyceps and recharge your batteries
Experience the invigorating power of nature and science. For new energy, strong blood vessels and mental freshness. Ideal for anyone who wants to get off to a powerful start.
The days are getting longer, the light is returning and now is the time to give your body a gentle boost. The combination of L-citrulline, an amino acid that promotes blood circulation, and the vital mushroom cordyceps supports you in a natural way. For more performance, better focus and an all-round vital body feeling.

Detox cure with L-arginine: Detoxify & recharge your energy
Find out how L-arginine supports your detoxification, boosts your metabolism and improves your athletic performance.
With a 5-day detox plan, you can cleanse your body in a targeted manner, promote blood circulation and increase your well-being. For more energy and an all-round good feeling!

The cardiovascular system: your engine for health and energy
Discover how your cardiovascular system ensures that nutrients and oxygen reach every cell every day – and why it is so important to keep it healthy.
The cardiovascular system is our body's vital transportation system. It delivers oxygen and nutrients to every cell, keeping us moving every day. Learn how it works and why keeping it healthy is so important.

Citrulline – the natural energy booster
Find out how citrulline can help support your performance and endurance in everyday life.
Citrulline can support your energy and endurance, promote recovery and improve blood flow. Discover how this amino acid derivative can help you in your daily life.

Proline: the building block for healthy joints
Discover the benefits of proline for your joints, skin and connective tissue.
Proline is an amino acid that plays an important role in healthy joints, skin and connective tissue. Find out how proline can help strengthen your joints and keep your skin elastic. Immerse yourself in the world of amino acids and their benefits for your health!
Say goodbye to stress - hello GABA!
Do you often feel stressed and overworked? GABA, a natural neurotransmitter, could be the solution. Find out how GABA helps your body to reduce stress, calm your nerves and promote a feeling of deep relaxation.

Ashwagandha - a real health all-rounder?
The powder from the sleeping berry is an integral part of Ayurvedic medicine and is valued for its many health-promoting properties. Read more now.
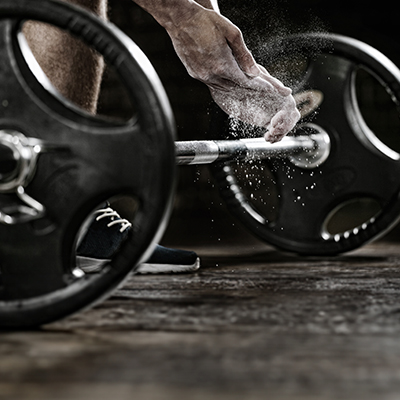

How creatine affects fitness
Creatine is primarily known for its effect on muscle building - but it plays a far more versatile role in the human body. We have summarised everything you need to know about this special substance for you in this article.
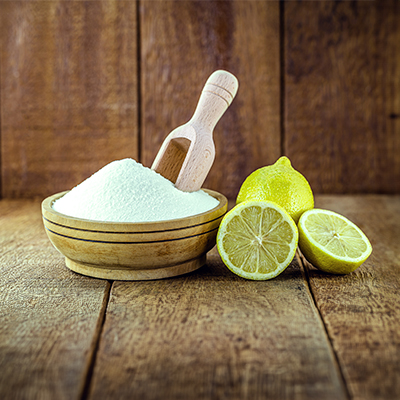

Home remedies for heartburn
Burning, heartburn, pain: almost everyone is familiar with heartburn. Taking a look at your lifestyle and diet can help manage the symptoms. Find out now how you can get relief in just a few steps!
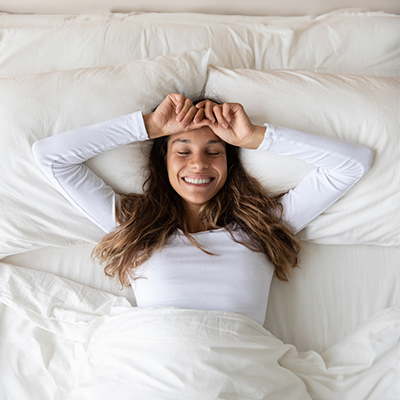

Glycine regenerates body and mind
As an important amino acid, glycine is involved in many processes in the body and can have a positive effect on both physical and mental health. Muscles, skin, stress and psyche: find out more about the extensive areas of application and effects of this amino acid here.
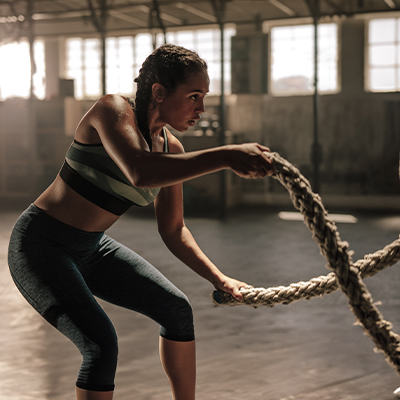

How L-carnitine works in energy metabolism
Carnitine is mainly found in animal foods and plays an important role in energy metabolism. Find out more now.
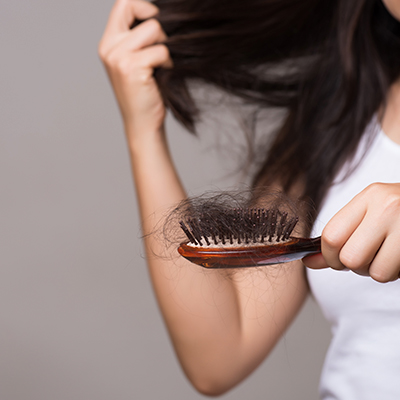

These are the causes of hair loss
There are many different types of hair loss in men and women - and there are different ways to help your hair grow back. Find out more now.
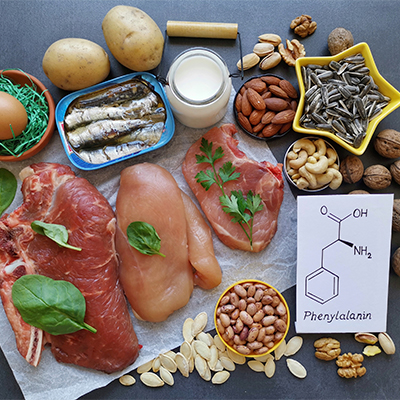

The body needs phenylalanine for this
The amino acid phenylalanine is required for the synthesis of dopamine and serotonin and is also an important building block for proteins. Find out more now.
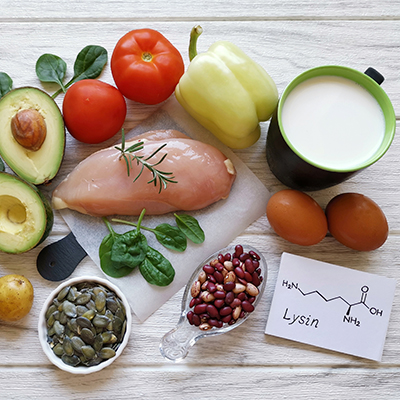

The essential amino acid lysine
From the metabolism to the immune system to the skin: there are many processes in the body in which lysine is involved. A deficiency of the essential amino acid can therefore disrupt these processes. The good news is that lysine is found in many foods. Find out more in this articel!

L-threonine - an essential amino acid with important functions
Amino acids are an important building block for our health. Which ones can the body produce and which ones need to be ingested in order to fulfil all functions? What are the risks for vegans and what are the dangers of a deficiency? Our report answers the most important questions!

The link between L-Arginine and women's health
The amino acid L-Arginine is primarily associated with muscle growth and improved endurance. Some studies suggest that it may also have a positive effect on women's health.

Fitter and stronger with L-Carnosine?
Although carnosine can be produced by the human body, it is a popular supplement among athletes - in powder or capsule form. In this article, you can find out what specific effects it has on performance and what other functions it is involved in.
The importance of amino acids for your body is undeniable. These organic compounds are fundamental to a variety of physiological processes. From building muscle to supporting the immune system, your body needs an adequate supply of amino acids to maintain its functions. Among the various amino acids, arginine and glycine are worth mentioning, both of which play important roles in the body. By ensuring that your body gets the amino acids it needs, you support its basic functions and contribute to your overall well-being.
Amino acids as food supplements - what you should consider
When taking food supplements with amino acids and/or vitamins, it is particularly important to pay attention to the quality and bioavailability of the products. High-quality supplements not only guarantee better tolerability, but also more effective absorption of the nutrients in the body. Make sure that the products come from trustworthy manufacturers and are tested according to strict quality standards. Good bioavailability ensures that the amino acids can be optimally absorbed and used by the body. This significantly increases their effectiveness.
What is the difference between non-essential and essential amino acids?
Essential amino acids are amino acids that cannot be produced by the human body itself. They must therefore be obtained from food. They are vital for various physiological functions - including building proteins and supporting the immune system. The essential amino acids include lysine, leucine, maline, threonine, methionine, phenylalanine and tryptophan.
Non-essential amino acids, on the other hand, can be synthesized by the body itself. This means that they do not necessarily have to be ingested through food, but can be produced by the body through other compounds. Non-essential amino acids include alanine, asparagine, aspartic acid, glutamine and glutamic acid. Although non-essential amino acids do not necessarily have to be ingested through food, they play an important role in metabolism and other functions in a healthy human body.
Semi-essential amino acids are those that the body can basically produce itself, but not always in sufficient quantities [1].
What amino acids are there and how do they work?
There are a variety of amino acids in the human body, including essential, semi-essential and non-essential amino acids. All of them play an important role for humans and contribute to various physiological processes ranging from muscle regeneration and immune function to mood and mental performance:
Essential amino acids
L-leucine: L-leucine is important for protein synthesis and plays a key role in building and maintaining muscle mass. It supports wound healing and regulates blood sugar levels. [1]
L-isoleucine: L-isoleucine supports muscle regeneration after training and contributes to energy production. It also helps with calcium absorption and supports the immune system. [2]
L-valine: L-valine is crucial for muscle metabolism and helps to regulate the nitrogen balance in the body. It also plays a role in providing energy and maintaining nitrogen balance in the body. [3]
L-lysine: L-lysine is important for collagen production, the maintenance of the immune system and the absorption of calcium. [4]
L-methionine: L-methionine is important for the production of cysteine and taurine, which contribute to detoxification and protection against oxidative stress. It also supports the health of skin, hair and nails. [5]
L-phenylalanine: L-phenylalanine is a precursor for the synthesis of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, serotonin and noradrenaline. It plays a role in the regulation of mood and mental performance. [6]
L-threonine: L-threonine is important for the formation of collagen and elastin, which support the skin and connective tissue. It also plays a role in the synthesis of antibodies that strengthen the immune system. [7]
L-tryptophan: L-tryptophan is a precursor of the neurotransmitter serotonin, which regulates mood and promotes a sense of well-being. It also helps in the production of melatonin, which regulates the sleep-wake cycle. [8]
Semi-essential amino acids
Histidine: Histidine is important for the growth and repair of tissues and for the formation of histamine, which is involved in allergic reactions. [9]
Non-essential amino acids:
Alanine: Alanine plays a role in energy metabolism and can serve as fuel for the muscles.
L-arginine: L-arginine is involved in the regulation of blood flow and can increase nitric oxide production, which can improve blood circulation. Arginine also supports the immune system and wound healing. [10]
Asparagine: Asparagine is important for the transport of nitrogen between tissues and organs.
Aspartic acid: Aspartic acid is involved in various metabolic pathways and can support energy production.
Cysteine: Cysteine is an important component of glutathione, a powerful antioxidant that prevents cell damage. [7]
L-glutamine: L-glutamine is important for intestinal health, the immune system and the maintenance of acid-base balance. [5]
Glutamic acid: Glutamic acid is a neurotransmitter that is involved in the transmission of nerve impulses.
Glycine: Glycine is involved in the synthesis of proteins, DNA and bile acids and acts as a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system.
Proline: Proline is important for the structure of collagen and other structural proteins in the body.
Serine: Serine is involved in the synthesis of phospholipids, which are components of cell membranes.
L-tyrosine: L-tyrosine is a precursor for the production of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, noradrenaline and adrenaline.
What is L-carnitine?
L-carnitine is not an essential amino acid, but a compound that can be synthesized from the two essential amino acids lysine and methionine. The body can produce L-carnitine in the liver and kidneys. The prerequisite for this is that sufficient amounts of lysine and methionine are present in the diet. In addition, the enzymes required for synthesis must be present in sufficient quantities.
In what forms are food supplements with amino acids available?
Food supplements with amino acids are available in various forms to suit different preferences and needs. Many of them are amino acid complexes, i.e. mixtures of different amino acids that are present in a certain ratio to each other.
Tablets and capsules
Advantages: Tablets and capsules are easy to take, easy to dose and have a long shelf life.
Disadvantages: Tablets and capsules may be difficult for some people to swallow and are absorbed more slowly by the body compared to other dosage forms.
Powder
Advantages: Powder is flexible in dosage, can be dissolved in water or other liquids and scores with rapid absorption.
Disadvantages: Taking powder requires some preparation. The taste can be unpleasant.
How does a lack of amino acids manifest itself?
- Delayed muscle building and muscle regeneration after training
- Reduced muscle mass and strength
- Increased susceptibility to muscle loss and muscle atrophy
- Slower metabolism and associated weight problems
- Reduced production of important hormones and neurotransmitters
- Reduced immune function and increased risk of infections
- Impaired wound healing and tissue repair
- Fatigue, lack of energy and reduced physical performance
- Mood problems such as depression, anxiety or irritability
- Impaired cognition and memory function
- Hair and skin problems, including brittle hair and dry skin
- Possible organ dysfunction [11]
What can impair the utilization of amino acids in the body?
The utilization of amino acids in the body can be impaired by various factors, including diseases of the digestive tract, metabolic disorders, liver and kidney problems, poor dietary habits or a lack of so-called enzymatic cofactors: Certain enzymes are often required for the synthesis and breakdown of amino acids, which in turn require certain cofactors, such as vitamins and minerals. A lack of these cofactors can impair the proper function of the enzymes and thus disrupt the utilization of amino acids.
What are amino acid complexes?
Amino acid complexes are mixtures of different amino acids that are present in a certain ratio to each other. They are often sold as food supplements and can be available in various forms such as powder, tablets or capsules.
The composition of an amino acid complex can vary depending on the product and can be tailored to specific needs. Some amino acid complexes contain a selection of non-essential and essential amino acids. Others focus on specific amino acids or combinations thereof. They are always intended for specific purposes, such as:
- Support for muscle development
- Improvement of athletic performance
- Promoting regeneration after training
- Increasing general health and well-being
Who should take amino acids?
It can be useful for:
- Athletes and fitness enthusiasts to support muscle building and recovery after training
- People with increased protein requirements, such as older people, pregnant women or people recovering from injury
- Vegetarians and vegans to ensure they get all essential amino acids
- People with certain health conditions such as liver or kidney problems to compensate for deficiencies or support health [12]
Can I lose weight with amino acids?
L-carnitine is believed to play a role in fat breakdown and energy production. It is said to help transport long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria, where they are burned to produce energy. [13]
In addition, amino acids can help to minimize muscle breakdown during a calorie-restricted diet, support the metabolism and increase the feeling of satiety. This in turn can help to support weight loss. [14]
Sources:
[1] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10418071
[2] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30843485
[3] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38093456
[4] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16636474
[5] https://www.thieme-connect.com/a-1251-6013
[6] https://www.mikronaehrstoffcoach.com/l-phenylalanin
[7] https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/L-threonine
[8] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/469515
[9] https://daminoc.com/histidin
[10] https://www.mikronaehrstoffcoach.com/l-arginin
[11] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/NBK557845
[12] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/NBK234922
[13] https://www.researchgate.net/L-carnitine-in-the-transport-of-long-chain-fatty-acids
[14] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32827096
